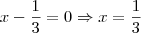Encontre os valores de a e b de modo que a função abaixo seja contínua.
g(x)= x^2 cos(a+b/x), se x for diferente de 0
b, se x=0



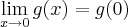 ,
, ...
...
 ,
,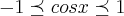 ,
,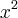 cresce mais que o cosx,pelo teorema do confronto,prevalece o valor de
cresce mais que o cosx,pelo teorema do confronto,prevalece o valor de 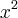
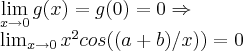
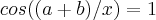 ou
ou 

![y=(a+b)/x\Rightarrow x\rightarrow 0,y\rightarrow \infty
\lim_{y\rightarrow \infty}g((a+b)/y)=\lim_{y\rightarrow\infty}{((a+b)/y)}^{2}cos(y)
=(a+b).\sqrt[]{(\lim_{y\rightarrow \infty})(1-{(seny)}^{2})/{y}^{4}} y=(a+b)/x\Rightarrow x\rightarrow 0,y\rightarrow \infty
\lim_{y\rightarrow \infty}g((a+b)/y)=\lim_{y\rightarrow\infty}{((a+b)/y)}^{2}cos(y)
=(a+b).\sqrt[]{(\lim_{y\rightarrow \infty})(1-{(seny)}^{2})/{y}^{4}}](/latexrender/pictures/e648ca632a95a55db97e39c83f067969.png)
![=(a+b)^2.\sqrt[]{(\lim_{y\rightarrow\infty}).(1/{y}^{2})(1/{y}^{2}-{(seny/y)}^{2}}=(a+b).\sqrt[]{0}=0
\Rightarrow {(a+b)}^{2}=0\Rightarrow a+b=0 =(a+b)^2.\sqrt[]{(\lim_{y\rightarrow\infty}).(1/{y}^{2})(1/{y}^{2}-{(seny/y)}^{2}}=(a+b).\sqrt[]{0}=0
\Rightarrow {(a+b)}^{2}=0\Rightarrow a+b=0](/latexrender/pictures/f2730327c6034a028a77a52a63fd28fd.png)
Voltar para Cálculo: Limites, Derivadas e Integrais
Usuários navegando neste fórum: Nenhum usuário registrado e 3 visitantes
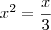
 .
.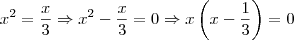
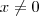 :
: