-
-
Novo APOIA.se AjudaMatemática
por admin em Sáb Abr 25, 2020 19:01
- 0 Tópicos
- 478185 Mensagens
-
Última mensagem por admin
em Sáb Abr 25, 2020 19:01
-
-
Agradecimento aos Colaboradores
por admin em Qui Nov 15, 2018 00:25
- 0 Tópicos
- 531945 Mensagens
-
Última mensagem por admin
em Qui Nov 15, 2018 00:25
-
-
Ativação de Novos Registros
por admin em Qua Nov 14, 2018 11:58
- 0 Tópicos
- 495474 Mensagens
-
Última mensagem por admin
em Qua Nov 14, 2018 11:58
-
-
Regras do Fórum - Leia antes de postar!
por admin em Ter Mar 20, 2012 21:51
- 0 Tópicos
- 706088 Mensagens
-
Última mensagem por admin
em Ter Mar 20, 2012 21:51
-
-
DICA: Escrevendo Fórmulas com LaTeX via BBCode
por admin em Qua Ago 29, 2007 04:04
- 41 Tópicos
- 2122263 Mensagens
-
Última mensagem por Janayna
em Qui Abr 27, 2017 00:04
 por guilherme5088 » Seg Mar 23, 2020 17:55
por guilherme5088 » Seg Mar 23, 2020 17:55
-
guilherme5088
- Usuário Ativo

-
- Mensagens: 22
- Registrado em: Seg Set 02, 2019 22:46
- Formação Escolar: GRADUAÇÃO
- Área/Curso: engenharia eletrica
- Andamento: cursando
 por guilherme5088 » Seg Mar 23, 2020 17:56
por guilherme5088 » Seg Mar 23, 2020 17:56
Verifique que *
Conclua que*
-
guilherme5088
- Usuário Ativo

-
- Mensagens: 22
- Registrado em: Seg Set 02, 2019 22:46
- Formação Escolar: GRADUAÇÃO
- Área/Curso: engenharia eletrica
- Andamento: cursando
Voltar para Cálculo: Limites, Derivadas e Integrais
Se chegou até aqui, provavelmente tenha interesse pelos tópicos relacionados abaixo.
Aproveite a leitura. Bons estudos!
-
- [Derivada Parcial de 1ª Ordem] - Derivada parcial num ponto
por Vitor2+ » Dom Jul 01, 2012 16:27
- 6 Respostas
- 4007 Exibições
- Última mensagem por e8group
Seg Jul 02, 2012 10:56
Cálculo: Limites, Derivadas e Integrais
-
- derivada parcial
por jmario » Dom Abr 18, 2010 11:41
- 0 Respostas
- 1541 Exibições
- Última mensagem por jmario
Dom Abr 18, 2010 11:41
Cálculo: Limites, Derivadas e Integrais
-
- Derivada Parcial
por Silva339 » Seg Mar 25, 2013 19:06
- 1 Respostas
- 1669 Exibições
- Última mensagem por DanielFerreira
Sex Mar 29, 2013 02:28
Cálculo: Limites, Derivadas e Integrais
-
- [Derivada Parcial]
por Russman » Qui Mar 28, 2013 22:04
- 1 Respostas
- 1334 Exibições
- Última mensagem por Russman
Sex Mar 29, 2013 13:00
Cálculo: Limites, Derivadas e Integrais
-
- [Derivada] derivada parcial verificação
por Marcelo_ribeiro » Seg Mar 26, 2012 13:57
- 4 Respostas
- 2789 Exibições
- Última mensagem por Marcelo_ribeiro
Ter Mar 27, 2012 02:28
Cálculo: Limites, Derivadas e Integrais
Usuários navegando neste fórum: Nenhum usuário registrado e 96 visitantes
Assunto:
Unesp - 95 Números Complexos
Autor:
Alucard014 - Dom Ago 01, 2010 18:22
(UNESP - 95) Seja L o Afixo de um Número complexo
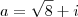
em um sistema de coordenadas cartesianas xOy. Determine o número complexo b , de módulo igual a 1 , cujo afixo M pertence ao quarto quadrante e é tal que o ângulo LÔM é reto.
Assunto:
Unesp - 95 Números Complexos
Autor:
MarceloFantini - Qui Ago 05, 2010 17:27
Seja
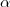
o ângulo entre o eixo horizontal e o afixo

. O triângulo é retângulo com catetos

e

, tal que

. Seja
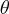
o ângulo complementar. Então
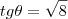
. Como
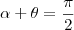
, o ângulo que o afixo

formará com a horizontal será
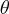
, mas negativo pois tem de ser no quarto quadrante. Se
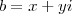
, então
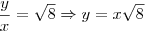
. Como módulo é um:
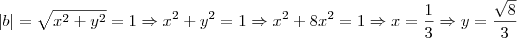
.
Logo, o afixo é
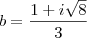
.
Powered by phpBB © phpBB Group.
phpBB Mobile / SEO by Artodia.





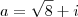 em um sistema de coordenadas cartesianas xOy. Determine o número complexo b , de módulo igual a 1 , cujo afixo M pertence ao quarto quadrante e é tal que o ângulo LÔM é reto.
em um sistema de coordenadas cartesianas xOy. Determine o número complexo b , de módulo igual a 1 , cujo afixo M pertence ao quarto quadrante e é tal que o ângulo LÔM é reto.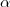 o ângulo entre o eixo horizontal e o afixo
o ângulo entre o eixo horizontal e o afixo  . O triângulo é retângulo com catetos
. O triângulo é retângulo com catetos  e
e  , tal que
, tal que  . Seja
. Seja 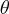 o ângulo complementar. Então
o ângulo complementar. Então  . Como
. Como 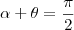 , o ângulo que o afixo
, o ângulo que o afixo  formará com a horizontal será
formará com a horizontal será 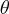 , mas negativo pois tem de ser no quarto quadrante. Se
, mas negativo pois tem de ser no quarto quadrante. Se 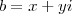 , então
, então 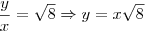 . Como módulo é um:
. Como módulo é um: 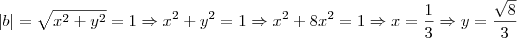 .
.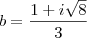 .
.